Starting Question
Let’s give five examples of artificial intelligence.
What is AI?
AI: Artificial Intelligence
It is the science and engineering of making intelligent machines, especially intelligent computer programs.
McCarthy, John. “What is artificial intelligence?.” (2007).
It is related to the similar task of using computers to understand human intelligence, but AI does not have to confine itself to methods that are biologically observable.
The research field of science and engineering, which devoted to building artificial animals and humans.
Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy
Are they “Artificial Intelligence”?
Consider whether the following system can be called “Artificial Intelligence.”
- A machine that buys you some bread that you might like at the push of a button.
- A machine that cooks rice at the push of a button
- A machine that produces a fixed amount of tea at the push of a button.
- A pen that ejects a wick at the push of a button
These are all a “push a button, then do X” system, but are they all Artificial Intelligence…?
What is intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence and Natural Intelligence
Natural Intelligence: The intelligence in humans, animals, and other living creatures.
Artificial Intelligence: Intelligent behavior demonstrated by machines (non-living creatures made by humans).
What is Intelligence?
This section is a summary of britannica.com
Psychologists generally do not characterize human intelligence by just one trait but by the combination of many diverse abilities.
Research in AI has focused chiefly on the following components of intelligence:
Learning
There are a number of different forms of learning as applied to artificial intelligence.
The simplest is learning by trial and error.
For example, a simple computer program for solving mate-in-one chess problems might try moves at random until mate is found.
The program might then store the solution with the position so that the next time the computer encountered the same position it would recall the solution.
Reasoning
To reason is to draw inferences appropriate to the situation.
Inferences are classified as either deductive or inductive.
Problem-solving
Problem-solving, particularly in artificial intelligence, may be characterized as a systematic search through a range of possible actions in order to reach some predefined goal or solution.
Problem-solving methods divide into special purposes and general purposes.
Some examples are finding the winning move (or sequence of moves) in a board game, devising mathematical proofs, and manipulating “virtual objects” in a computer-generated world.
Perception
In perception, the environment is scanned by means of various sensory organs, real or artificial, and the scene is decomposed into separate objects in various spatial relationships.
An analysis is complicated by the fact that an object may appear different depending on the angle from which it is viewed, the direction and intensity of illumination in the scene, and how much the object contrasts with the surrounding field.
At present, artificial perception is sufficiently well advanced to enable optical sensors to identify individuals, autonomous vehicles to drive at moderate speeds on the open road, and robots to roam through buildings collecting empty soda cans.
Language (symbol manipulation)
A language is a system of signs having meaning by convention.
In this sense, language need not be confined to the spoken word. T
Strong AI vs. Weak AI
Strong AI
Strong artificial intelligence (AI), also known as artificial general intelligence (AGI) or general AI, is a theoretical form of AI used to describe a certain mindset of AI development.
If researchers are able to develop Strong AI, the machine would require an intelligence equal to humans; it would have a self-aware consciousness that has the ability to solve problems, learn, and plan for the future.
Weak AI
Weak AI, also known as narrow AI, focuses on performing a specific task,
such as answering questions based on user input or playing chess.
It can perform one type of task, but not both, whereas Strong AI can perform a variety of functions, eventually teaching itself to solve for new problems.
Weak AI relies on human interference to define the parameters of its learning algorithms and to provide the relevant training data to ensure accuracy.
While human input accelerates the growth phase of Strong AI, it is not required, and over time, it develops a human-like consciousness instead of simulating it, like Weak AI.
Self-driving cars and virtual assistants, like Siri, are examples of Weak AI.
The five examples you gave at the beginning of this class are Weak AI? or Stong AI?
Sensory Motor System
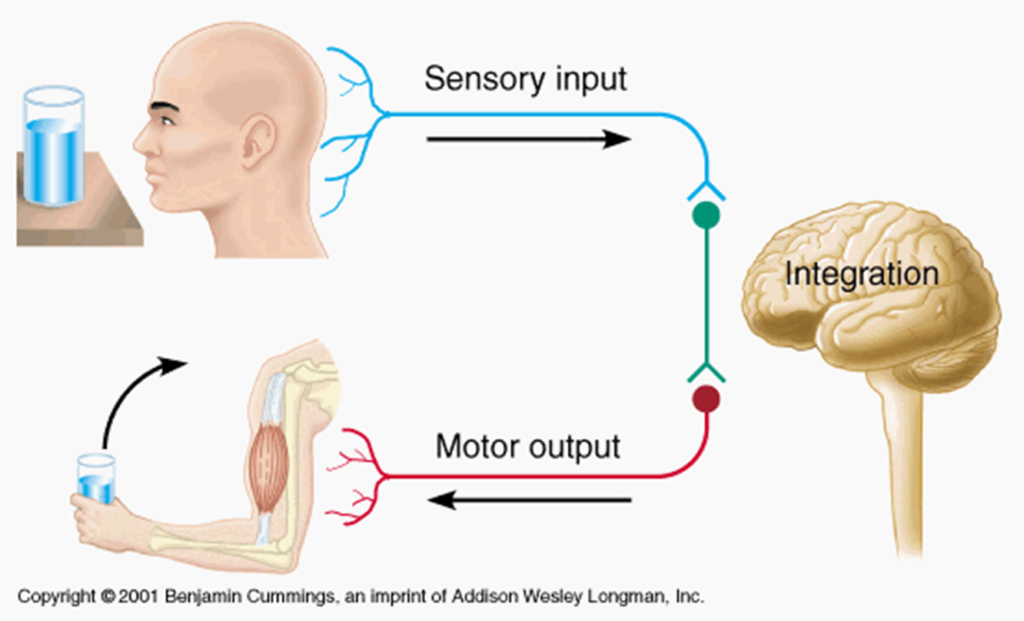
Sensor
Computer
Actuator
Reference: Useful websites
Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy: Artificial Intelligence
IBM: IBM Cloud Learn Hub / What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?